Table Of Content

During the analysis of study data, multivariate analysis (usually logistic regression) can be used to adjust for the effect of measured confounders. A cohort study compares the experience of 2 or more groups of patients who are followed concurrently forward in time (Figure 1). While one may be added if the investigator so chooses, members of the cohort are primarily selected because of a shared characteristic among them. In particular, retrospective cohort studies are designed to follow a group of people with a common exposure or risk factor over time and observe their outcomes. Case-control studies are a type of observational study often used in fields like medical research, environmental health, or epidemiology.
case-control study
The risk of melanoma also increased with increase in years of use, hours of use, and sessions. Keep in mind that by definition the case group is chosen because they already possess the attribute of interest. The point of the control group is to facilitate investigation, e.g., studying whether the case group systematically exhibits that attribute more than the control group does.
Disadvantages of case-control studies
Since the OR is greater than 1, the outcome is more likely in those exposed (those who are diagnosed with metabolic syndrome) compared with those who are not exposed (those who do are not diagnosed with metabolic syndrome). However, we will require confidence intervals to comment on further interpretation of the OR (This will be discussed in detail in the biostatistics section). They can be particularly useful when we are interested in trying to ensure that some of the measurable and non-measurable confounders are relatively equally distributed in cases and controls (such as home environment, socio-economic status, or genetic factors). The next important point in designing a case-control study is the selection of control patients.
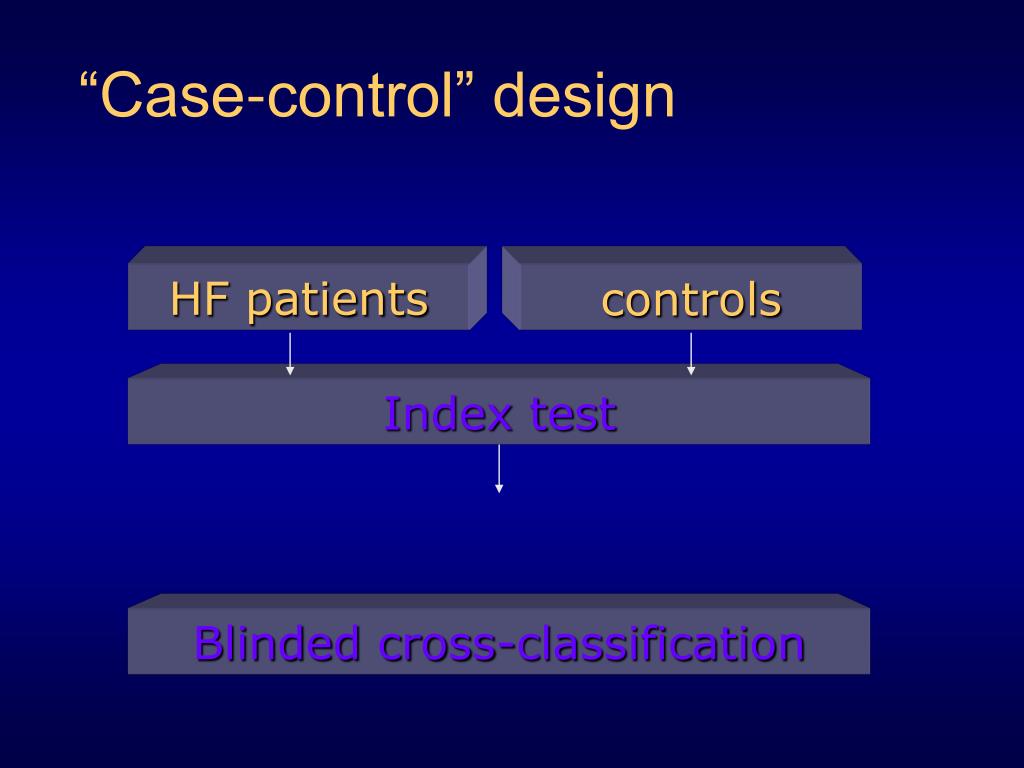
What is a case-control study?
The 1167 cases - individuals with invasive cutaneous melanoma – were selected from Minnesota Cancer Surveillance System. The 1101 controls were selected randomly from Minnesota State Driver's License list; they were matched for age (+/- 5 years) and sex. In their landmark study, Doll and Hill (1950) evaluated the association between smoking and lung cancer. A case-control study differs from a cross-sectional study because case-control studies are naturally retrospective in nature, looking backward in time to identify exposures that may have occurred before the development of the disease. Since we considered arbitrary intervals between time points and because, in real-world studies, time is never measured in a truly continuous fashion, this does not represent an important limitation for practical purposes. It is however important to note that the intervals between interventions and outcome assessments (in a target trial) are an intrinsic part of the estimand that lies at the start of investigation.
Case-control sampling
Case-control studies are beneficial for an initial investigation of a suspected risk factor for a condition. The information obtained from cross-sectional studies then enables researchers to conduct further data analyses to explore any relationships in more depth. A case-control study is a research method where two groups of people are compared – those with the condition (cases) and those without (controls). By looking at their past, researchers try to identify what factors might have contributed to the condition in the ‘case’ group. There is a suspicion that zinc oxide, the white non-absorbent sunscreen traditionally worn by lifeguards is more effective at preventing sunburns that lead to skin cancer than absorbent sunscreen lotions. A case-control study was conducted to investigate if exposure to zinc oxide is a more effective skin cancer prevention measure.
This ensures a smooth transition for experienced colorists while offering a user-friendly introduction for beginners. Case Design Corporation (CDC) is a privately owned and operated business serving the industry for over 90 years. The solution provides the ability to collect evidence once and map it across multiple regulations – simplifying compliance to multiple regulations.
Case–control study of paternal occupational exposures and childhood bone tumours and soft-tissue sarcomas in Great ... - Nature.com
Case–control study of paternal occupational exposures and childhood bone tumours and soft-tissue sarcomas in Great ....
Posted: Wed, 26 Feb 2020 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Wacholder and colleagues (1992 a, b, and c) have published wonderful manuscripts on design and conduct of case-control of studies in the American Journal of Epidemiology. The data were collected by self administered questionnaires and telephone interviews. The investigators assessed the use of tanning devices (using photographs), number of years, and frequency of use of these devices. They also collected information on other variables (such as sun exposure; presence of freckles and moles; and colour of skin, hair, among other exposures. Supplementary material to ‘Identification of causal effects in case-control studies’.
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study. The authors have no personal, financial, or institutional interest in any of the drugs, materials, or devices described in this article. A case-control study of readmission to the intensive care unit after cardiac surgery. In addition, case-control studies look at a single subject or a single case, whereas longitudinal studies can be conducted on a large group of subjects.
Extreme sampling design in genetic association mapping of quantitative trait loci using balanced and unbalanced case ... - Nature.com
Extreme sampling design in genetic association mapping of quantitative trait loci using balanced and unbalanced case ....
Posted: Tue, 29 Oct 2019 07:00:00 GMT [source]
In causal inference, it is important that the causal question of interest is unambiguously articulated [1]. The causal question should dictate, and therefore be at the start of, investigation. When the target causal quantity, the estimand, is made explicit, one can start to question how it relates to the available data distribution and, as such, form a basis for estimation with finite samples from this distribution.
Case-control studies are advantageous because they require smaller sample sizes and thus fewer resources and less time than other observational studies. The case-control design also is the most practical option for studying exposure related to rare diseases. Case-control studies also are used for diseases that have long latent periods (long durations between exposure and disease manifestation) and are ideal when multiple potential risk factors are at play. Pharmacists use knowledge from cohort and case–control studies to inform patients, clinicians, and the general public about drug effects. At a basic level, cohort and case–control studies quantitatively estimate the relation between exposures and outcomes. They represent rigorous study designs for answering drug safety and effectiveness questions, with case–control studies being more prone to bias.
Case-control studies are different from cross-sectional studies in that case-control studies compare groups retrospectively while cross-sectional studies analyze information about a population at a specific point in time. Forming an accurate control group can be challenging, so sometimes researchers enroll multiple control groups to bolster the strength of the case-control study. If the exposure is found more commonly in the cases than the controls, the researcher can hypothesize that the exposure may be linked to the outcome of interest. Case Control Studies are prospective in that they follow the cases and controls over time and observe what occurs.


No comments:
Post a Comment